« Deploy React Application using Docker and Google Cloud Platform
February 5, 2019 • ☕️ 4 min read
In this article, you will learn how to deploy applications on GCP. We will deploy a create-react-app.
Link to the Repo — https://github.com/Harshmakadia/react-docker
Before we get started with the actual steps of deploying the React App using GCP and Docker. First, let’s understand what docker actual is?
Docker is a tool which is designed to make the creating, deploying and running of applications easier with the help of containers. Containers are something which allows the developer to bundle the application with all the necessary ingredients like different libraries, dependencies and ship is as only a single package.
We will go step by step
1. Creating React Application
Create react app is a lot easier using the create-react-app (CRA)
We will use create-react-app package to install and configure simple react application from NPM, Open your terminal and install react app.
For more info on creating a react app
facebook/create-react-app
_Set up a modern web app by running one command. Contribute to facebook/create-react-app development by creating an…_github.com
once you run the application using command
$ npm start
After that, it’s time to create a build the app, run
$ npm run build
2. Creating minimal Dockerfile
creating a docker file is a cup of your tea. The is no rocket science in creating a docker file.
Just Create a new file with name Dockerfile
Now once the file is created we will add some command to that which will help us to create, run, deploy the application.
Here the content of Dockerfile for react app. Note I’m using Nginx to as a server.
Dockerfile
Once the docker file is created. I’m creating a new folder named deployment within the app directory which has a nginx.conf file
The content of nginx file, note that this is default configuration you may not need to alter this file unless you have some special requirements.
nginx.conf
3. Installing Docker on your machine
Head to this link below and download it for your respective operating system
Docker Desktop
_Docker Desktop Enterprise is a new commercial desktop offering that gives you everything you need for enterprise-ready…_www.docker.com
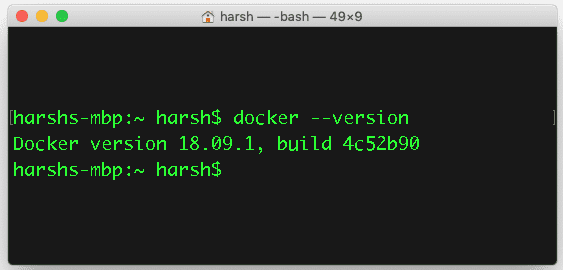
Once it is installed run open your terminal and run below command to check it is installed successfully
docker — — version
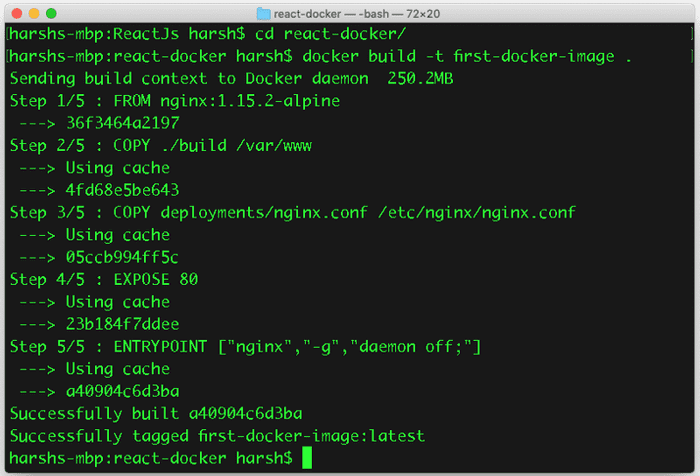
Now that we have the docker setup on our machine it’s time to create the first image using the following command
docker build -t first-docker .
more info about different command can be found here.
Once you run this command it will execute all the command listed down in the Dockerfile.
we have successfully created the image. Let’s proceed to next step
4. Make use of gcloud SDK
Download SDK from the below link and setup on your machine
Cloud SDK | Cloud SDK | Google Cloud
_A collection of command line tools for the Google Cloud Platform. Includes gcloud, bq, gsutil and other important…_cloud.google.com
Now that we have the gcloud SDK setup on our machine
- — Create a new project in GCP
Next step is to create a new project in the GCP where we will be pushing our docker images to the containers.
Configure Docker to use gcloud as a credential helper or are using another authentication method. To use gcloud as the credential helper, run the command:
gcloud auth configure-docker
It’s time to push the image to the registry
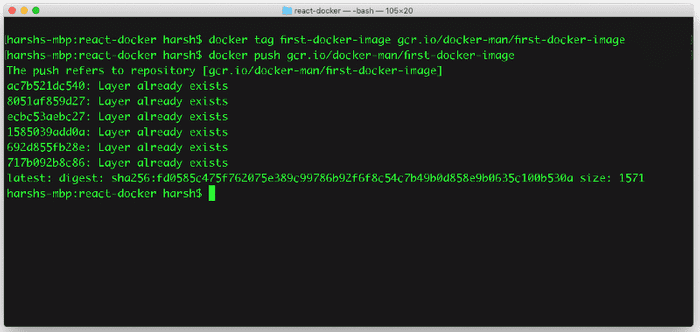
- Tag the local image with the registry name by using the command:
docker tag [SOURCE_IMAGE] [HOSTNAME]/[PROJECT-ID]/[IMAGE]
- where
[SOURCE_IMAGE]is the local image name. - This command names the image with the registry name and applies the tag
latest. If you want to apply a different tag, then use the command:
docker tag [SOURCE_IMAGE] [HOSTNAME]/[PROJECT-ID]/[IMAGE]:[TAG]
Push the tagged image to Container Registry
Push the tagged image to Container Registry by using the command:
docker push [HOSTNAME]/[PROJECT-ID]/[IMAGE]
This command pushes the image that has the tag latest. If you want to push an image that has a different tag, use the command:
docker push [HOSTNAME]/[PROJECT-ID]/[IMAGE]:[TAG]
When you push an image to a registry with a new hostname, Container Registry creates a storage bucket in the specifiedmulti-regional location. After pushing your image, you can:
- Go to the GCP Console to view the registry and image.
- Run
gcloud container images list-tagsto view the image’s tag(s) and automatically-generated digest: gcloud container images list-tags [HOSTNAME]/[PROJECT-ID]/[IMAGE]- The command’s output is similar to the following:
DIGEST TAGS TIMESTAMP 44bde... test 2017-..-..
Where
[HOSTNAME]is listed under Location in the console. It’s one of four options:gcr.io,us.gcr.io,eu.gcr.io, orasia.gcr.io.[PROJECT-ID]is your Google Cloud Platform Console project ID. See Domain-scoped projects for how to work with projects IDs that include a domain.[IMAGE]is the image’s name in Container Registry.[TAG]is the tag applied to the image. In a registry, tags are unique to an image.
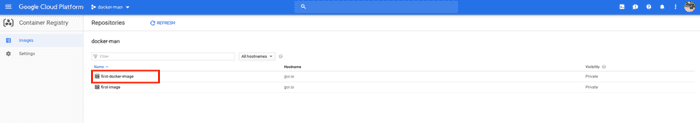
Navigate the GCP console and search of Container Registry, you will be able to see the image which we push.
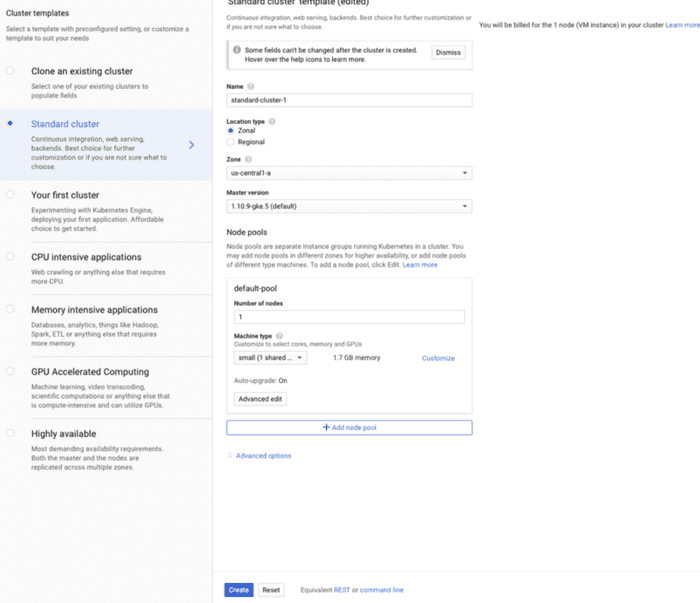
It’s time to create cluster now inside Kubernetes Engine in GCP
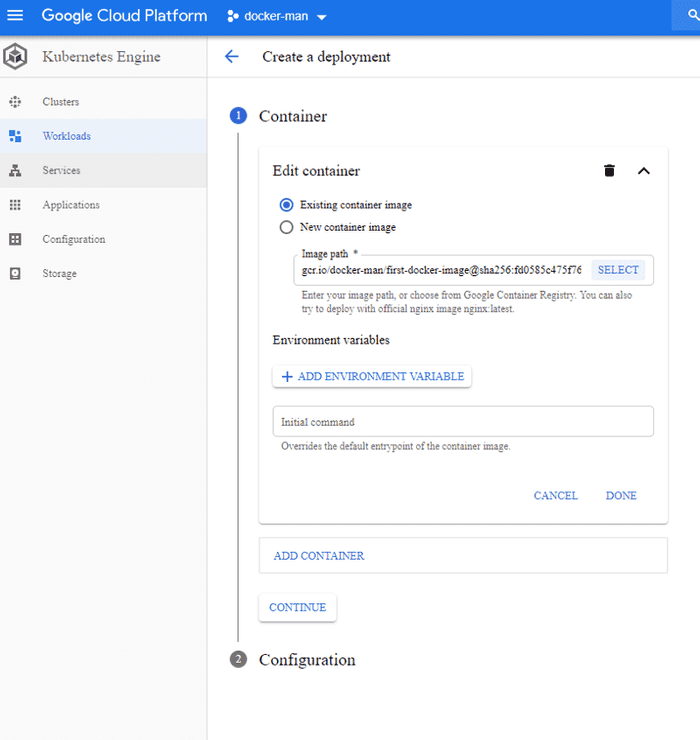
Create deployment under workloads
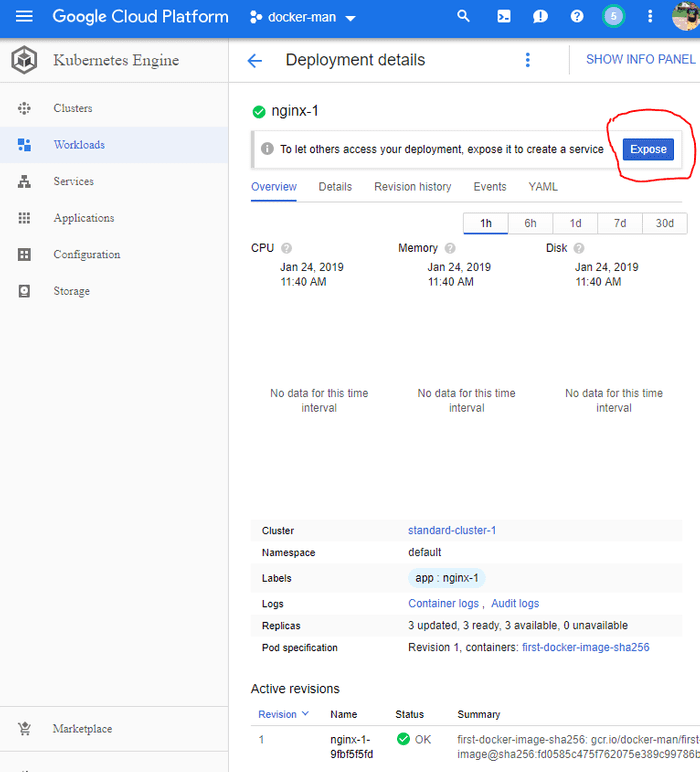
Select the image which you want to deploy and finally click on Expose to expose the deployment.
Set port to 80 in Target Port since we had EXPOSED our application to 80 in the Dockerfile
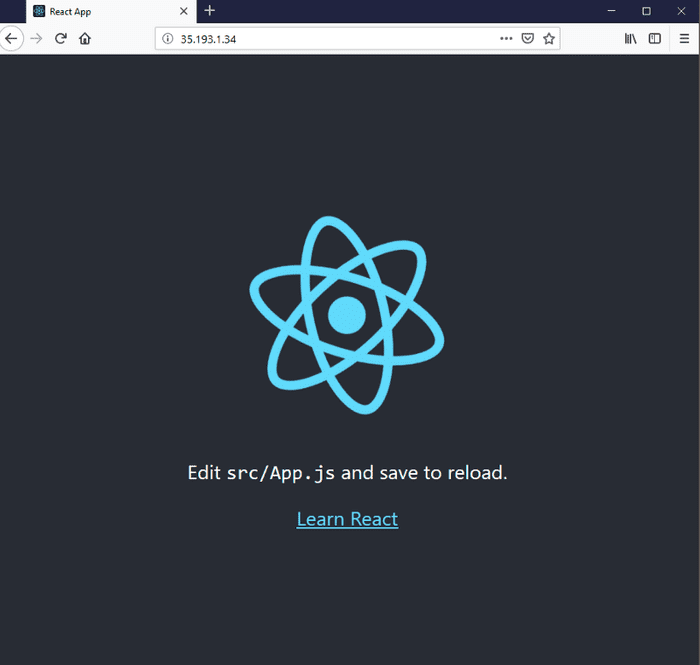
Once you have exposed the port you will get IP Adress where your react application will be running live.
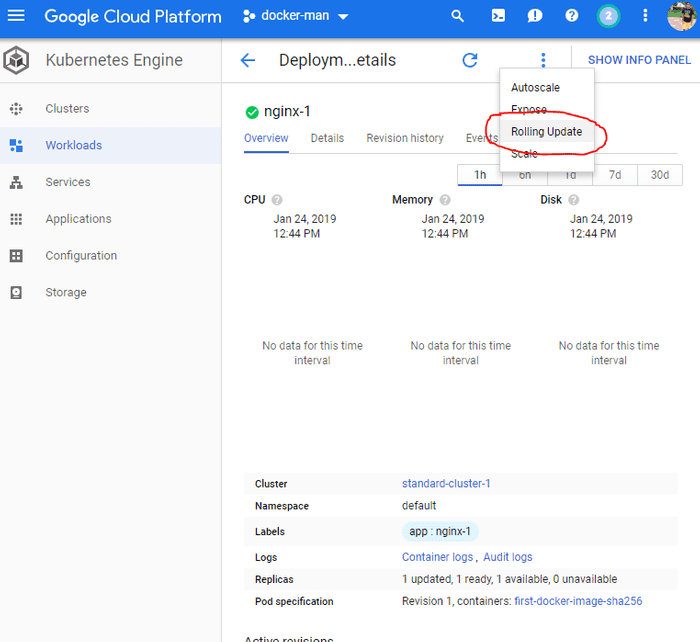
And that it’s you are all set with docker. Whenever you want to push new image to the container first build the image with above-specified commands and then push the image to container registry and finally make that image live by going to rolling update option.
Please note down your questions in the comment section below if you have any doubts & I’ll be happy to address them.
That’s the end 🔚 I hope you have learned something new.
Happy Learning! 💻 😃